About The Product
Descripción
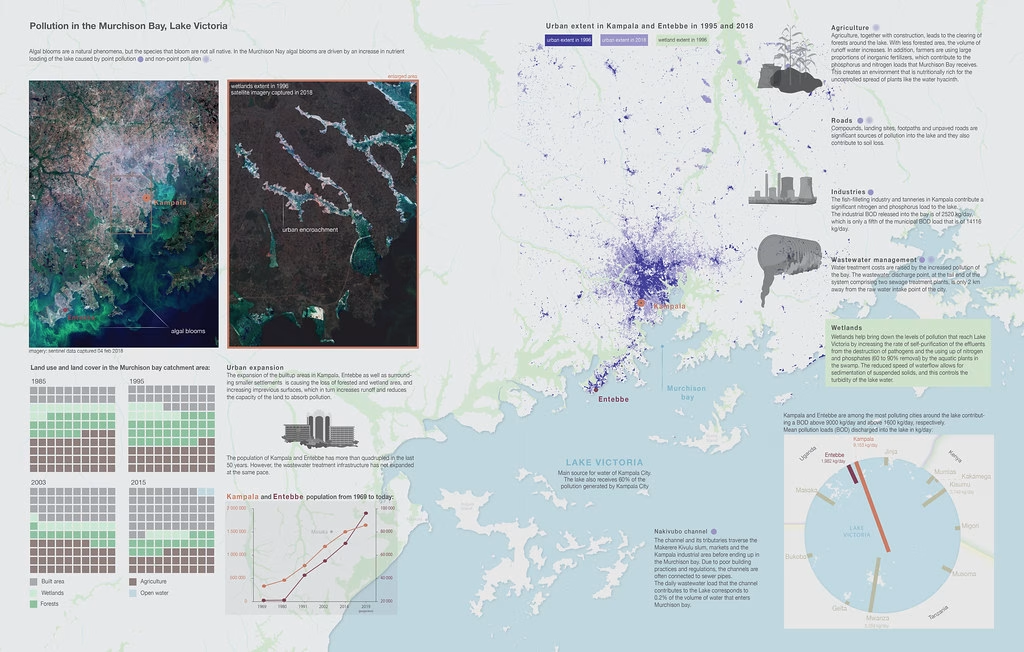
At 68,800 km2, Lake Victoria is Africa’s largest freshwater lake, whose shoreline is shared by the East African states of Kenya (6 per cent), Uganda (45 per cent) and Tanzania (49 per cent). Pollution, mainly resulting from increased human activities such as discharge of wastes, has resulted in severe eutrophication and dramatically low dissolved oxygen levels, with up to half of its 500+ species of endemic cichlid fish likely to become extinct. Through effective operation of existing treatment facilities alone, organic loads on the Kenyan side could be reduced by 50 per cent. Such continuing degradation of Lake Victoria’s ecological functions has serious long-term consequences for the ecosystem services it provides and poses a threat to social welfare in the countries bordering its shores. Sources: Verschuren et al. (2002); Scheren et al. (2000)
Información adicional
| Language | English |
|---|---|
| Publisher | GRID-Arendal |
| Language | Inglés |